All trips

Visa & Health
Formalities
Addresses of consulates
- British Embassy in EthiopiaComoros Street Addis Ababa 858 EthiopiaAddis AbabaTel. : +251 11 6170100Fax :
- Embassy of Ethiopia, London17 Princes Gate, Knightsbridge, London SW7 1PZ, UKSW7 1PZ LondonTel. : +44 20 7589 7212
Health
Insurance
Voltage
In Ethiopia, power plugs and sockets (outlets) of type C, type E, type F and type L are used. The standard voltage is 220 V at a frequency of 50 Hz.
Budget and money
Telephone and jetlag
Country information
Country ID
Socio-economical data
History
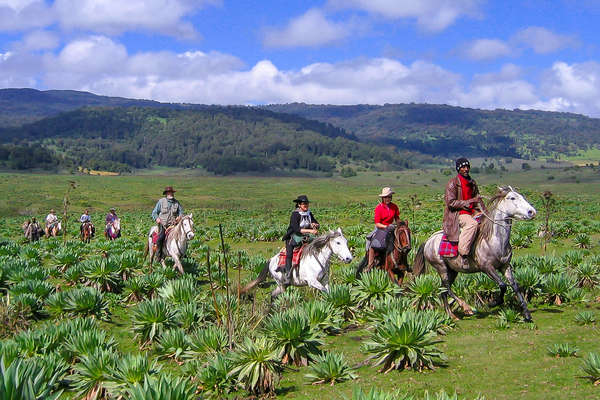
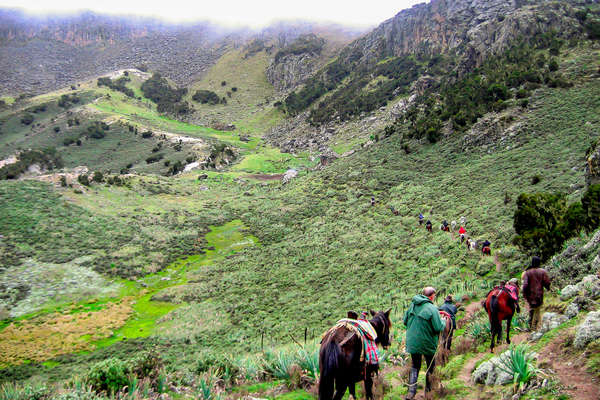
Geography
People, culture and traditions
Ethiopia’s culture is as diverse as its people, with over 80 ethnic groups, each contributing distinct languages, music, dance, and customs. The country is famous for its ancient Orthodox Christian heritage, exemplified by the rock-hewn churches of Lalibela, and its claim to being the birthplace of coffee. Festivals such as Timkat (Epiphany) and Meskel (Finding of the True Cross) highlight the spiritual depth of Ethiopian society, with vibrant processions and traditional attire.
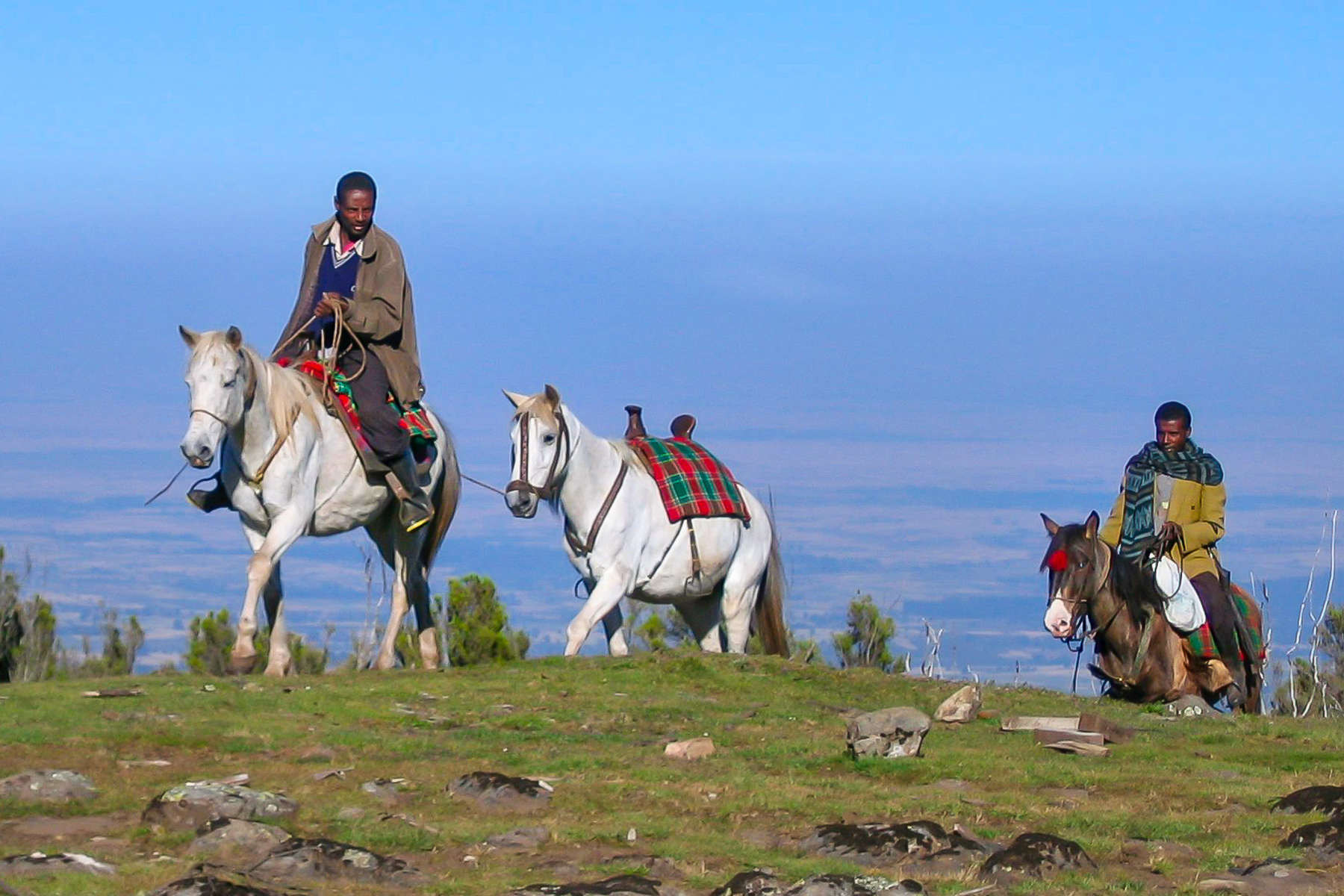
Horses have held a central place in Ethiopian history and culture, as a symbol of power, prestige, and skill. Equestrianism was historically tied to the country’s military power. Emperors such as Menelik II and Haile Selassie were often depicted on horseback, showcasing the status and importance of equines in Ethiopian society.
Traditional equestrian games and displays remain an integral part of cultural celebrations in rural areas. One such tradition is the Gugs, a horseback performance in which riders demonstrate their prowess by galloping and skillfully throwing spears or shields. These events are not only entertaining but also a way to honor Ethiopia’s warrior heritage.
Horses are also deeply embedded in everyday rural life, where they serve as essential companions for farming, transportation, and community connection. The highland regions, in particular, are known for their tough and resilient horses, well-suited to the rugged terrain.